Telco 2.0™ Research
The Future Of Telecoms And How To Get There
The Future Of Telecoms And How To Get There
|
Summary: Although telcos aren’t generally associated with disruption, many operators around the world have attempted to disrupt adjacent markets, such as digital commerce, entertainment and financial services. In some cases, telcos have even disrupted their core broadband and communications markets. While many of these moves have fizzled out or have flown below investors’ radar screens, several have had a major impact on both the telco’s revenues and relevance. These include SK Planet, M-Pesa, Au Smart Pass and BT Sport. Why do some disruptive moves by telcos succeed and others fail? (January 2015, Dealing with Disruption Stream) |
|
Below is an introductory extract and list of contents from this 41 page Report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the Dealing with Disruption stream here.
(NB. This report is only available to members of our Dealing with Disruption Stream - members of other streams or the Executive Briefing Service please email for more information).
For more on any of these services, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003
Part of STL’s new Dealing with Disruption in Communications, Content and Commerce stream, this executive briefing explores the role of telcos in disrupting the digital economy. It analyses a variety of disruptive moves by telcos, some long-standing and well established, others relatively new. It covers telcos’ attempts to reinvent digital commerce in South Korea and Japan, the startling success of mobile money services in east Africa, BT’s huge outlay on sports content, AT&T’s multi-faceted smart home platform, Deutsche Telekom’s investments in online marketplaces and Orange’s innovative Libon communications service.
In each case, this briefing describes the underlying strategy, the implementation and the results, before setting out STL’s key takeaways. The conclusions section outlines the lessons other would-be disruptors can learn from telcos’ attempts to move into new markets and develop new value propositions.
Note, this report is not exhaustive. The examples it covers are intended to be representative. Part 2 of this report will analyse other telcos who have successfully disrupted adjacent markets or created new ones. In particular, it will take a close look at NTT DOCOMO, Japan’s leading mobile operator, which has built up a major revenue stream from new businesses. DOCOMO reported a 13% year-on-year increase in revenues from its new businesses in the six months to September 30th 2014 to 363 billion Japanese yen (more than US$3 billion). Its target for the full financial year is 770 billion yen (almost US$6.5 billion). Revenues from its Smart Life suite of businesses, which provide consumers with advice, information, security, cloud storage and other lifestyle services, rose 18% to 205 billion yen in the six months to September 30th 2014, while its dmarket content store now has 7.8 million subscribers. In the six months to September 30th, the total value of dmarket transactions rose 30% year-on-year to 34.6 billion yen.
In South Korea, leading telco KT is trying to use smartphone-based apps and services to disrupt the digital commerce market, as are the leading U.K. and U.S. mobile operators through their respective Weve and Softcard joint ventures. In the Philippines, Smart Communications and Globe Telecom have recast the financial services market by enabling people to send each other money using text messages.
Several major telcos are seeking to use their network infrastructure to change the game in the cloud services market. For example, U.S. telco Verizon has made a major push into cloud services, spending US$1.4 billion to acquire specialist Terremark in 2011. At the same time, Verizon and AT&T are having to respond to an aggressive play by T-Mobile USA to reshape the U.S. telecoms market with its Un-carrier strategy.
Some of these companies and their strategies are covered in other STL Partners reports, including:
In the digital economy, innovative start-ups, such as Spotify, Twitter, Instagram and the four big Internet platforms (Amazon, Apple, Facebook and Google) are generally considered to be the main agents of disruption. Start-ups tend to apply digital technologies in innovative new ways, while the major Internet platforms use their economies of scale and scope to disrupt markets and established businesses. These moves sometimes involve the deployment of new business models that can fundamentally change the modus operandi of entire industries, such as music, publishing and video gaming.
However, these digital natives don’t have a monopoly on disruption. So-called old economy companies do sometimes successfully disrupt either their own sector or adjacent sectors. In some cases, incumbents are actually well placed to drive disruption. As STL Partners has detailed in earlier reports, telcos, in particular, have many of the assets required to disrupt other industries, such as financial services, electronic commerce, healthcare and utilities. As well as owning the underlying infrastructure of the digital economy, telcos have extensive distribution networks and frequent interactions with large numbers of consumers and businesses.
Although established telcos have generally been cautious about pursuing disruption, several have succeeded in creating entirely new value propositions, effectively disrupting either their core business or adjacent industry sectors. In some cases, disruptive moves by telcos have primarily been defensive in that their main objective is to reduce churn in the core business. In other cases, telcos have gone on the offensive, moving into new markets in search of new revenues (see Figure 1).
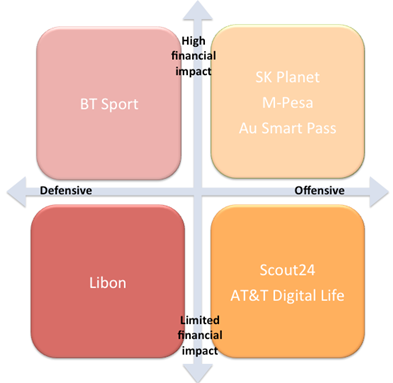
Source: STL Partners
The next section of this paper explores the disruptive moves in the top right hand corner of Figure 1 – those that have taken telcos into new markets and have had a significant financial impact on their businesses.
A classic disruptive play is to use existing assets and customer relationships to move into an adjacent market, open up a new revenue stream and build a major business. This is what Apple did with the iPhone and what Amazon did with cloud services. Several telcos have also followed this playbook. This section looks at three examples - SK Telecom’s SK Planet, Safaricom’s M-Pesa and KDDI’s au Smart Pass – and what other companies in the digital economy can learn from these largely successful moves. Unlike many disruptive moves by telcos, the three businesses covered in this section have had sufficient impact to properly register on investors’ radar screens. They have moved the needle for their parent’s telcos and given their investors confidence in their ability to innovate.
Owned by SK Telecom, SK Planet is a major broker in South Korea’s world-leading mobile commerce market. It has developed several two-sided online services that are similar in some respects to those offered by Google. SK Planet operates the T Map, a turn-by-turn navigation service, the T Store Android app store, the Smart Wallet payment, loyalty and couponing service, the OK Cashbag loyalty marketing programme and the 11th St online marketplace.
Strategy
Taking advantage of South Koreans’ appetite for new technologies, SK Telecom is using its home market as a test bed for mobile commerce solutions that could be deployed more widely. As well as seeking to generate revenues from enabling payments, advertising, loyalty, couponing and other forms of direct marketing in South Korea, it is aiming to become a leading mobile commerce player in other markets in Asia and North America.
SK Telecom’s approach has been to launch services early and then refine these services in response to feedback from the Korean market. It launched a mobile couponing service, for example, as early as 2008. To reduce the impact of corporate bureaucracy, in 2011, SK Telecom placed its digital commerce activities into a separate company, called SK Planet. The new entity has since focused on the development of a two-sided platform that aims to provide consumers with convenient shopping channels and merchants and brands with a wide range of marketing solutions both online and in the bricks and mortar arena. Although its services are over-the-top, in the sense that they don’t require consumers to use SK Telecom, SK Planet continues to work closely with SK Telecom - its sole owner.
Downstream, SK Planet is trying to differentiate itself by putting consumers’ interests first, giving them considerable control and transparency over the digital marketing they receive. Upstream, SK Planet is putting a lot of emphasis on helping traditional bricks and mortars stores go digital and reverse so-called showrooming, so that consumers research products online, but actually buy them from bricks and mortar retailers.
SK Planet CEO Jinwoo So talks about enabling “Next Commerce” by which he means the seamless integration of online and bricks and mortar commerce. “Just as Amazon became the global leader in e-commerce by revolutionizing the industry, SK Planet aims to
become the global ‘Next Commerce’ leader in the offline market by driving mobile innovation that will eventually
break down the walls which separate the online and offline worlds,” he says.
Estimating the offline commerce market in South Korea is worth 230 trillion won (more than 210 US billion dollars), SK Planet is aggressively adapting its existing digital commerce platforms, which are underpinned by SK Telecom’s network assets, for mobile commerce. It is also making extensive use of the big data generated by its existing platforms to hone its offerings.
At the 2014 Mobile World Congress, SK Planet CEO Jinwoo So outlined how SK Planet has worked closely with SK Telecom to develop algorithms that use customer data to predict churn and provide personalized recommendations and offers. “We combined the traditional data mining with text mining,” he said. “How people create the search criteria or the sites they visit, we came up with a very unique formula, which gives up much two times better performance than before. … In 11th street, we have achieved almost three times better performance by applying our recommendation engine, which we developed. Now we are trying to prove the ROI for marketing budgets for brands and merchants.”
To access the rest of this 41 page Disruption Report in full, including...
…and the following figures…
...Members of the Dealing with Disruption Stream can download the full 26 page report in PDF format here. Non-Members, please subscribe here. For other enquiries, please email [email protected] / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003
Technologies and industry terms referenced include: Disruption, innovation, smartphones, Internet of Things, smart homes, mobile wallets, localized commerce, location based services, personal data, telco strategy, big data, mobile commerce, digital commerce, APIs, business models, SoLoMo, mobile advertising, mobile marketing, mobile payments, SK Planet, M-Pesa, Au Smart Pass, BT Sport, KDDI, Deutche Telecom, Scout 24, AT&T, Digital Life, KT, NTT, Docomo...