|
Summary: The unveiling of Apple Pay and unravelling of Weve (the UK operators’ payments venture) looked like bad news for telcos’ ambitions in mobile payments in some markets, and highlighted challenges to Google and others’ models. Yet there are already successful telco models and favourable market trends that telcos should exploit. So what are the opportunities now? (September 2014, Executive Briefing Service, Dealing with Disruption Stream.) |
|
Below is an extract from this 26 page Telco 2.0 Report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing service and the Dealing with Disruption Stream here.
We'll also be exploring the implications at Digital Asia (2-4 December, Bali), and are initiating coverage of a new research programme on Internet-Driven Disruption, and we'd really appreciate your input here. For more on any of these services, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003
After many years of trials, pilots and uncertainty, the mobile industry is now making a major push to enable consumers to use their mobile phones to complete transactions in stores and other merchant venues. This year is shaping up to be a pivotal year with a number of major launches of commercial mobile payment services involving device makers, mobile operators, the payment networks and retailers.
Crucially, Apple’s move to add Near Field Communications (NFC) – a short-range communications technology – to iPhone 6 has vindicated the telecoms industry’s ongoing push to make NFC a de facto standard for mobile proximity payments. Although sceptics (including Apple executives) have previously derided the cost and complexity of the technology, Vodafone, Orange, China Mobile and other major telcos have continued to develop digital commerce propositions based on the technology.
Apple’s U-turn on NFC has changed the sentiment around the technology dramatically and given the industry a clear sense of direction. Just a year ago, research firms, such as Gartner and Juniper, scaled back their forecasts for the use of mobile handsets to complete transactions in-store, primarily because Apple didn’t include a NFC chip in the iPhone 5.
The widespread use of NFC in stores will add fuel to the mobile payments market which is already growing rapidly. Some analysts are predicting mobile phones will be used to make transactions totalling more than US$721 billion worldwide by 2017 up from US$235 billion in 2013 (see Figure 1). Note, these figures include both remote/online and proximity/in-store transactions.
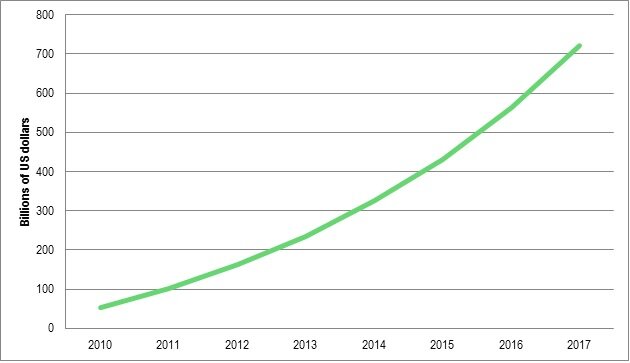
Source: Gartner; Goldman Sachs (via Statista)
Although most consumers are happy paying in store using either cash or payment cards, there are two major reasons why mobile payments are gaining momentum in an increasingly digital economy:
Consumers will want to be able to receive and redeem offers, vouchers and loyalty points using their smartphones. A mobile payment service would enable them to do this in a straightforward way.
Mobile payments will generate valuable transaction data that could and should (with the consumer’s permission) be used to make highly personalised recommendations and offers.
In other words, mobile payments are an essential element of a compelling integrated digital commerce proposition.
Although the big picture for mobile payments is improving, telcos are in danger of being side-lined in developed countries in this strategically important sector. (NB See the STL Partners Strategy Report, Digital Commerce 2.0: New $50bn Disruptive Opportunities for Telcos, Banks and Technology Players for a detailed study of how telcos could disrupt the key digital commerce brokers: Amazon, Google, Apple and Facebook.) In recent weeks, telcos’ efforts to lead the development of the mobile payments market suffered two major setbacks. Firstly, Apple’s fully formed mobile payments solution, called Apple Pay, effectively cuts telcos out of the mobile payments business in the Apple ecosystem.
Secondly, it emerged that Weve, the ground-breaking mobile commerce joint venture between U.K. mobile operators, has pulled back from plans to facilitate payments (in addition to its existing role of delivering targeted offers to UK mobile users). As a rare example of a well thought through collaborative venture between mobile operators, Weve had been a promising initiative that could provide a playbook for collaboration among mobile operators in other developed markets. But Weve’s change of course suggests that mobile operators are still struggling to collaborate effectively in the digital commerce market.
The Apple Pay proposition
Unveiled along with the iPhone 6 and the Apple Watch in September, Apple Pay is an end-to-end mobile payments proposition developed by Apple. On the device side, the basic technical architecture is similar to that advocated by major telcos via the industry group the GSMA – the short-range wireless technology Near Field Communications (NFC) is used to transfer payment data from the device to the point of sale terminal, while a secure element (a segregated memory chip) is used to protect sensitive information from being hacked or corrupted by third-party apps. However, rather than using telcos’ SIM cards as a secure element, Apple has added its own dedicated piece of hardware to the iPhone 6 and bolstered security further with a fingerprint scanner.
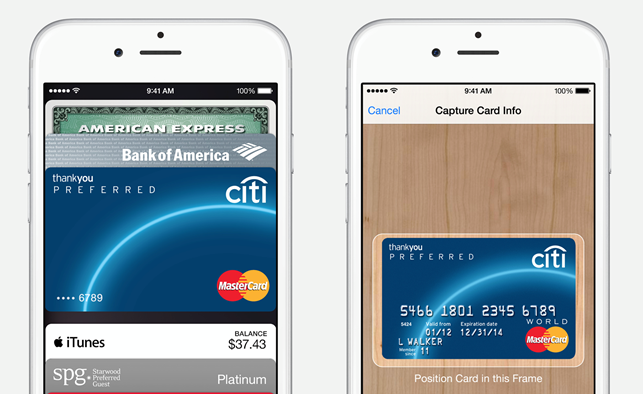
Already used to organise boarding passes, tickets, coupons and other collateral, Apple’s Passbook acts as the primary interface for the Apple Pay service. In other words, Passbook is now a fully-fledged mobile wallet. Thanks to its iTunes service, Apple already has hundreds of millions of consumers’ credit and debit card details on file. These consumers can add a compatible payment card stored on iTunes to Passbook simply by entering the card security code. Alternatively, they can use the iPhone camera to scan a payment card into a handset or type in the details manually. If the consumer stores more than one card, Passbook allows them to change the default payment card that appears when they are about to make a transaction.
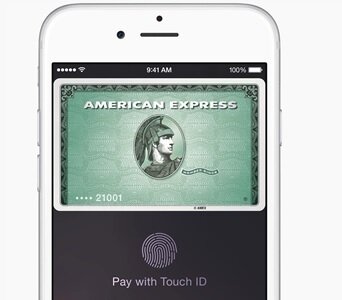
To make a payment in a store, the consumer simply holds their iPhone next to a NFC-enabled reader (attached to a point of sale terminal) with their finger on the handset’s Touch ID – the fingerprint reader embedded into the latest iPhones (see Figure 3). Unlike some mobile payment solutions, the consumer doesn’t need to open an app or enter a PIN code. The iPhone vibrates and beeps once the payment information has been sent. In this case, the payment information is protected by three layers of security: More than any existing mainstream mobile payments solution, including the SIM-secured NFC payments touted by telcos. These three layers are
Rather than transferring actual payment card details, Apple Pay transfers so-called tokens: a device-specific account number, together with a one-time security code.
These tokens are encrypted and stored on a secure element inside the iPhone – memory that is ring-fenced from access by any app other than Passbook. They aren’t stored on Apple’s servers, so are protected from online hacking.
The payment only happens if the Touch ID system recognises the consumer’s fingerprint, proving the consumer’s was in the store.
If the consumer is using an Apple Watch, which also has a NFC chip and a secure element, they hold the face of the watch near the reader and double-click a button on the side of the watch. As the range of NFC is just a few centimetres, consumers will have to hold the face of their watch against the reader. This step doesn’t sound very intuitive and may cause confusion in stores.
Again, a vibration and beep confirm the transfer of the payment information. Note, the watch needs to have been linked to an iPhone with a compatible payment card stored in a Passbook app. Although Apple Watch isn’t equipped with the Touch ID fingerprint scanner in the iPhone, it does have alternative security mechanisms built in. Apple Watch is equipped with a biosensor that can detect when the watch is taken off and lock its payment function, according to a report by NFC World. Apparently, consumers will have to enter a code to re-enable the payment function when they put the handset back on. These extra steps suggest making payments using Apple Watch will be more cumbersome and potentially less secure than using an iPhone 6 to make a payment.

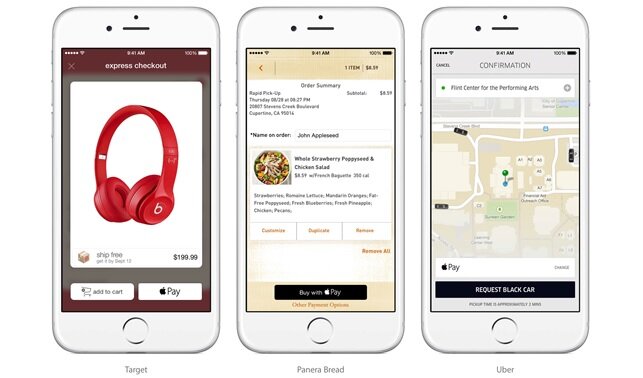
Apple Pay can also be used to make online payments in compatible apps and this is how many consumers are likely to try the service initially. Apple said that several merchants, including Disney, Starbucks, Target and Uber, have adapted their apps to accept Apple Pay transactions (see Figure 5). In this case, the consumer selects Apple Pay and then places their finger on the Touch ID interface. Note, enabling online payments is an area that has been neglected by many telcos in developed countries targeting this market, but support for remote payments is an essential component of any holistic digital commerce solution - consumers won’t want to use different digital wallets online and offline.
If a consumer loses their iPhone, then they can use the Find My iPhone service to put their device into “lost mode” or they can opt to wipe the handset. The next time the iPhone goes online, it will be frozen or wiped, depending on the option the consumer selected. Note, this feature negates one of the advantages of using a SIM card, which can also be wiped remotely by a telco, as a secure element.
Although the consumer’s most recent purchases will be viewable in Passbook, Apple says it won’t save consumer’s transaction information. This is in stark contrast to the approach taken by Apple’s own iTunes service and Amazon, for example, which uses a consumer’s transaction history to make personalised product and service recommendations. With Apple Pay, it seems a consumer will only be able to check historic transactions by looking at their bank statements.
The big guns in the U.S. financial services industry are supporting Apple Pay – consumers can use credit and debit cards from the three major payment networks, American Express, MasterCard and Visa, issued by a range of leading banks, including Bank of America, Capital One Bank, Chase, Citi and Wells Fargo, representing 83% of credit card purchase volume in the US, according to Apple, which says additional banks, including Barclaycard, Navy Federal Credit Union, PNC Bank, USAA and U.S. Bank, are also planning to sign up. This is a much greater level of participation than that achieved by Softcard (formerly known as Isis), the mobile commerce joint venture between U.S. telcos AT&T Mobile, Verizon Wireless and T-Mobile USA (see next section for more on Softcard).
Apple says that more than 220,000 bricks and mortar stores will accept Apple Pay transactions. Some of the participating retailers include leading brands, such as McDonalds, Stables, Subway, ToysRUs and Walgreens. However, the retailers in the Merchant Customer Exchange (MCX) consortium, which is developing its own mobile commerce proposition, have not signed up to accept Apple Pay. These retailers include major players, such as WalMart, Best-Buy, 7-11, Gap and Sears. (See next section for more on MCX). Although only a handful of apps are supporting Apple Pay today, that number is likely to grow rapidly, as many consumers will find it easier to press the Touch ID than to type in a password.
To access the rest of this 28 page Telco 2.0 Report in full, including...
...and the following report figures...
...Members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing Subscription Service and the Dealing with Disruption Stream can download the full 26 page report in PDF format here. Non-Members, please subscribe here. For other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
Industry terms referenced include: API, Big Data, Business Models, Digital Commerce, Localized Commerce, Location Based Services, Mobile, Advertising, Commerce, Marketing, Payments, Wallets, New Digital Economics, Personal Data, SoLoMo, Telco, Strategy, Disruption, Transformation, Innovation, Telecom.