Telco 2.0™ Research
The Future Of Telecoms And How To Get There
The Future Of Telecoms And How To Get There
|
Below is a major extract from this 18 page Telco 2.0 Analyst Note that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing service and the Telco 2.0 Dealing with Disruption Stream using the links below. 'Growing the Mobile Internet' and 'Fostering Vibrant Ecosystems: Lessons from Apple' are also key session themes at our upcoming 'New Digital Economics' Brainstorms (Palo Alto, 4-7 April and London, 11-13 May). Please use the links or email contact@telco2.net or call +44 (0) 207 247 5003 to find out more. |
For Amazon, the world of downloading and streaming brings both threats and opportunities: threats in that a large proportion of its current business is at risk of being cannibalised; and opportunities in that a significant element of its cost base associated with the storing, shipping, picking and packing of physical goods could be automated and reduced further.
Amazon’s key strengths are the size of its customer base; its ongoing relationships with all the major content owners in all the key categories (Books, Music, Movies/TV and Games); and most importantly, Amazon is the most highly skilled retailer on the Internet. Amazon’s Achilles heel is that it has very little control over next generation devices, apart from the Kindle, whether Tablet or Mobile phone.
In this note, we examine:
Amazon’s Operating Income in 2010 was $1.4bn with a typically low retail sector margin of 4.1%. This is a far lower margin than usually sought by the content industry, networks or the device industry and one of Amazon’s key strategic advantages – its investors do not expect huge margins. However, they do expect revenue growth and this it has delivered so far (see below) through the development of the most advanced retail platform on the Internet, fierce price competition, tight control over costs and increasing product diversification.
Figure 1: Amazon Operates with the Low Margins Typical of Retail
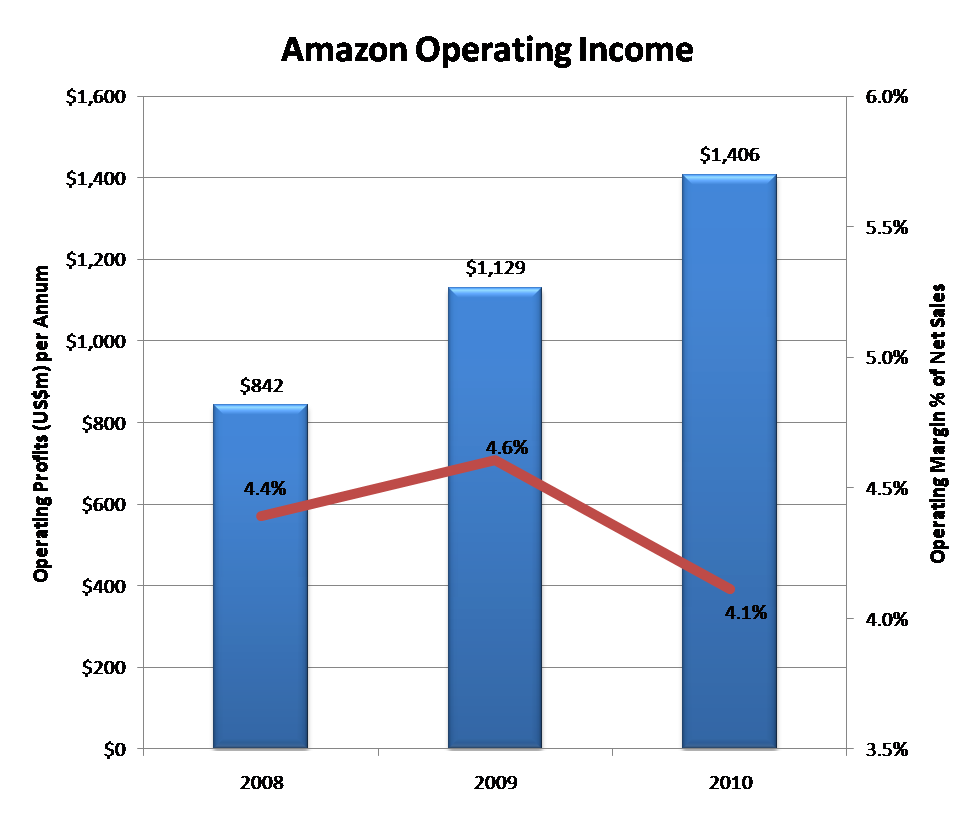
Source: Amazon, STL Partners
Amazon is now the world’s largest e-commerce site selling over US$34bn worth of goods and services in 2010. The Amazon main website attracts more unique visitors in a month than either eBay or Apple (see below).
Figure 2: Amazon is the busiest online store in the world
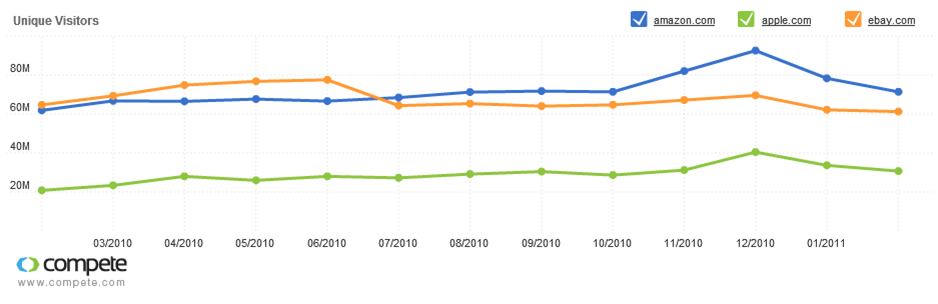
At the end of 2010, Amazon had over 130m ‘active’ customer accounts, a healthy increase of over 25 million in the year. In comparison Apple has over 200m accounts with credit cards stored - but does not break-out the percentage of these that are actually buying goods and services from it. It is therefore difficult to determine whether Amazon or Apple have the most paying customers passing through their stores. Whichever is the larger, Amazon’s retail prowess cannot be ignored, especially in entertainment media where its revenues continue to grow year-on-year.
Amazon’s roots are in selling books but over the years its portfolio has been extended successfully to other type of physical media so that its media category now comprises Books, Music, Movies, Video Games and Consoles, Software and Digital Downloads in most territories (USA, Canada, UK, Germany, France, Italy, Japan and China). The sales associated with its media business are still growing by over 10% per annum and, although declining as a percentage of total sales, still represented over 43% of total net sales in 2010. The reduction in percentage of total sales is therefore more a reflection of Amazon’s success in its diversified product range than any drop off in media.
Figure 3: Amazon’s media sales are still growing at over 10% per annum
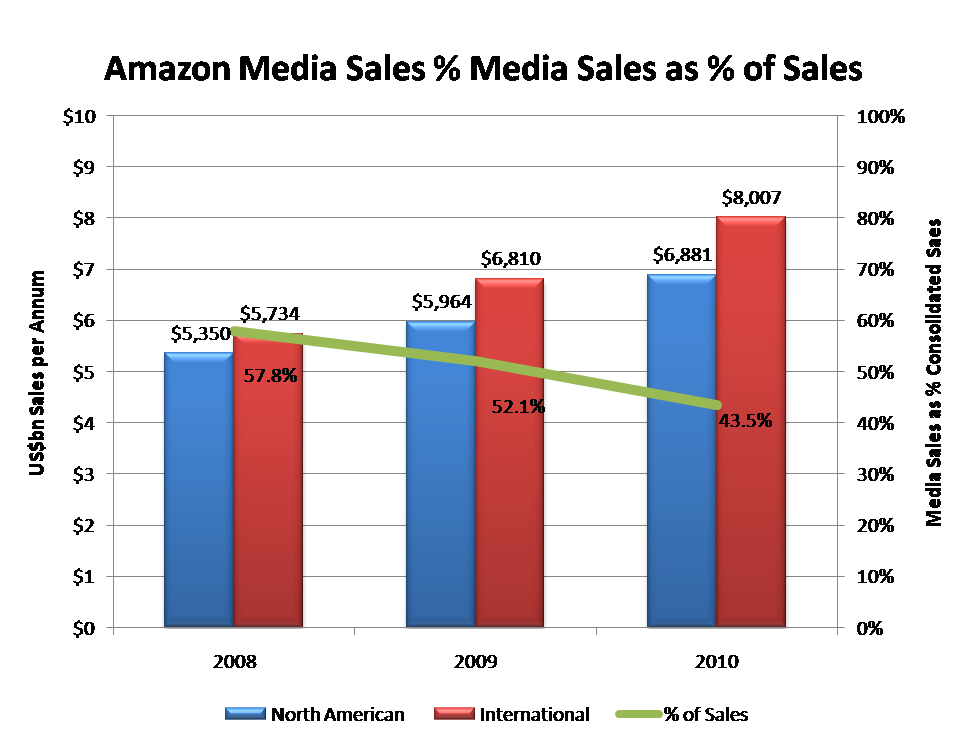
Source: Amazon, STL Partners
It is noteworthy that Amazon doesn’t provide any further detail on the media category and therefore little is known outside of Amazon about how their customers’ habits are changing from physical media consumption to digital. However, Amazon has been very clear that it sees a future where media is consumed both physically and digitally. In short, it wants to grow the entire pie and Amazon is not abandoning the physical world in much the same way that Netflix is not abandoning the mailing of DVDs.
Amazon promotes itself to investors as growing the absolute level of Operating Income and therefore is less worried about margins than overall growth. This is important for content owners as it aligns with their priorities and means that Amazon is as concerned with cannibalisation of physical product revenues as they are. However, that does not mean Amazon is in anyway anti-online distribution.
Amazon is also highly focussed on growing Free Cash Flow per share which implies strict management of working capital and balance sheet expenditure and to understand the appeal of online business in this context, we first have to understand the costs and cost trends associated with physical products.
Amazon currently spends about US$1.4bn or 4% of revenues on the physical shipping of goods to its customers. Despite Amazon’s famed distribution efficiency, this percentage has increased over the last couple of years, eating ever further beyond the associated shipping revenues, as illustrated below.
Figure 4: Amazon’s Net Shipping Costs Continue to Rise Over and Above P&P Charges to Consumers
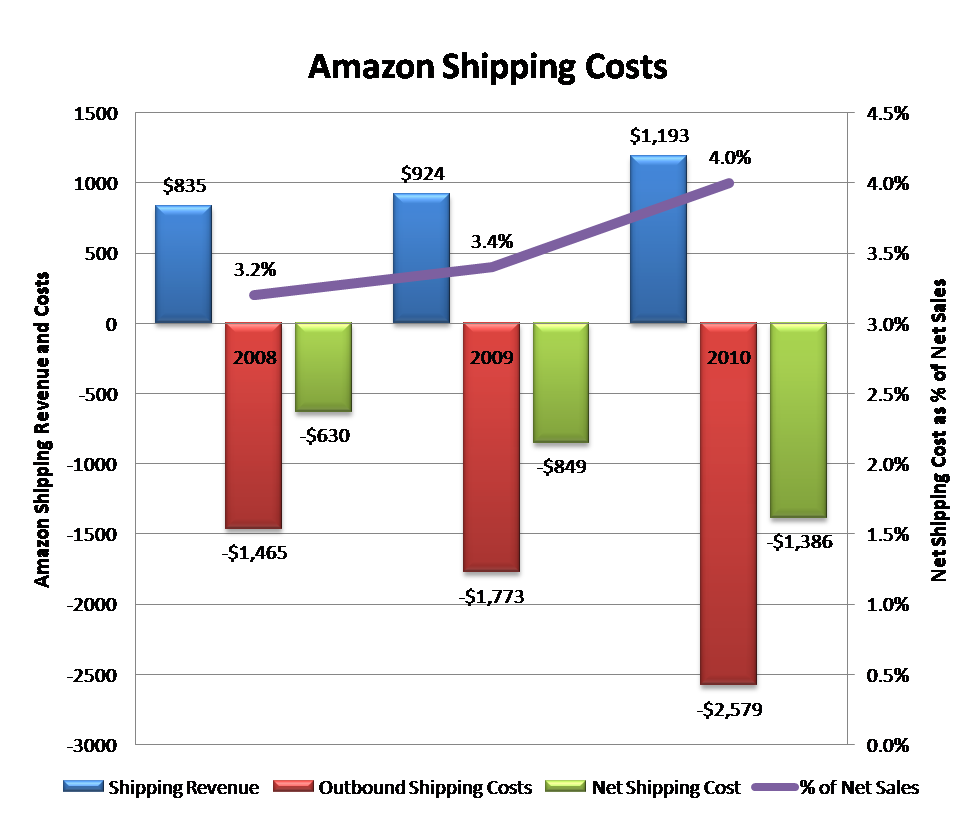
Source: Amazon, STL Partners
This is probably down to two factors:
Furthermore, there are additional costs associated with physical distribution.
Figure 5: Physical fulfilment costs Remain Stable as a Percentage of Net Sales
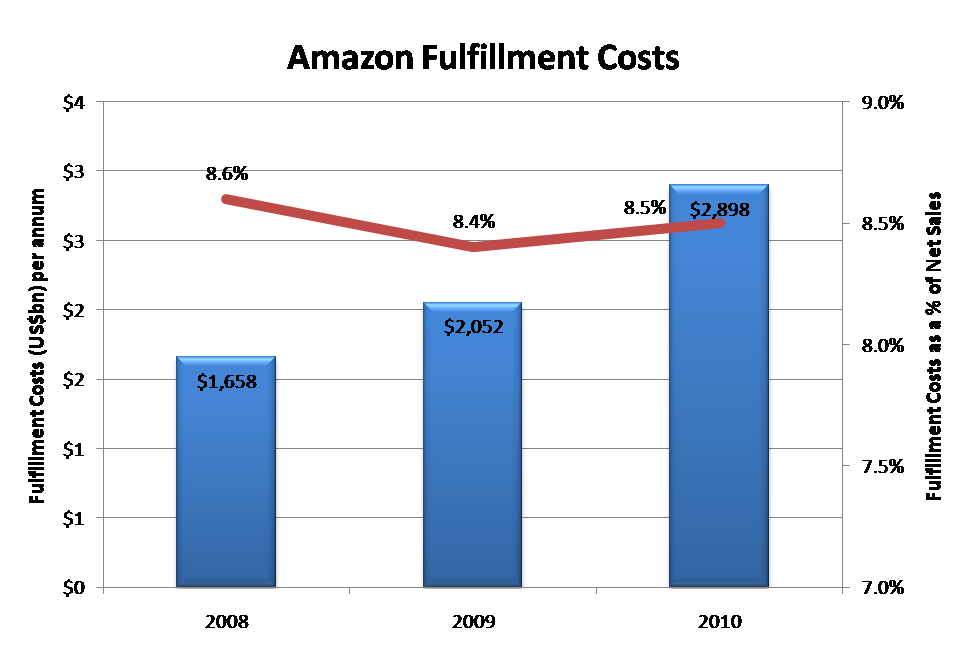
Source: Amazon, STL Partners
Amazon spent around US$2.9bn or 8.5% of revenues in 2010 on fulfilment costs (or the picking and packing) of goods. Amazon doesn’t break-out how much it spends on payment processing (included within cost of goods sold) or maintaining the technology (elements include Technology and Content, Depreciation and Amortisation) for its various e-commerce sites.
With Amazon’s ability to manage the combined physical costs of shipping and fulfilment to 12.5% of revenues in 2010, we believe that Amazon should be able to deliver online distribution for less than the 30% benchmark ‘agency fee’ revenue share typical in the online distribution model. And, that is before the additional efficiencies that Digital distribution offers over Physical. Therefore the margins offered up by the digital environment are highly attractive to Amazon.
Furthermore digital goods, in the main, fit perfectly into Amazon’s Operating Income growth model as the carrying cost of inventory is minimal and cash for goods is received immediately from customers, while the payment to content owners is typically dispersed 30-days after purchase. The major exception to this rule is when content owners demand large upfront fees for either access to content libraries or for exclusive deals. This is a major feature of both the Movies/TV and Music industry and may account at least in part for the differing levels of take up Amazon has experienced between these and e-books.
So, where does Amazon sit in online distribution – streaming and downloading? Is it a major player that needs to be actively worked with or against or can it be left out of the strategic thinking of the others in the digital online ecosystem – content owners, network service providers and device manufacturers? A closer examination of the position of Amazon in each of the major digital content categories – publishing, music, video and apps, provides valuable insight.
Amazon launched the Kindle in 2007 as an e-ink book reader for an introductory price of US$399, which in its first iteration had connectivity exclusively provided through the Sprint CDMA network. However, Amazon developed more than a hardware device with the Kindle, it built the whole surrounding ecosystem for sale, delivery and management of mainly electronic books but also other publishing media such as newspapers.
Figure 6: The Amazon Kindle
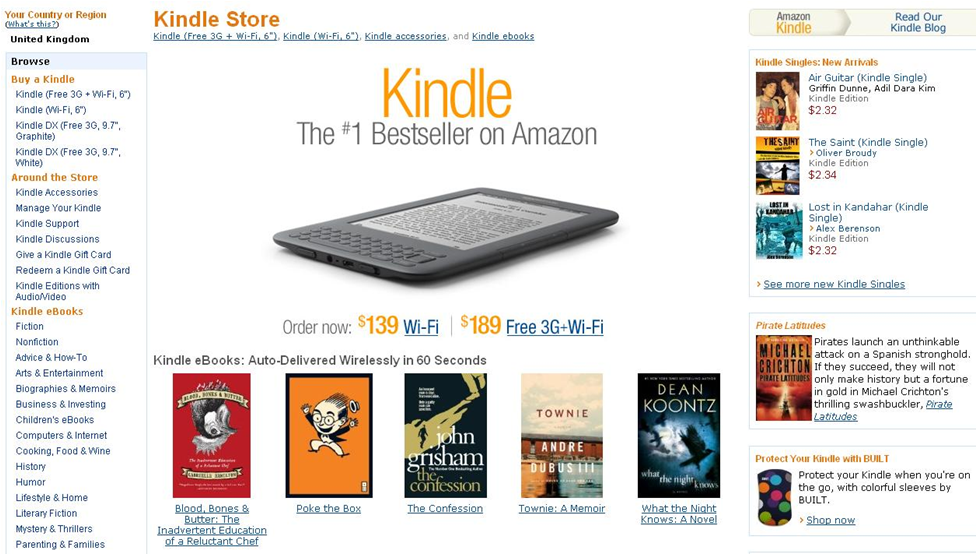
Today, the hardware price of the Kindle has come down to US$139 (WiFi only) to US$189 (WiFi+3G) and Amazon has launched Kindle readers across all the major platforms from Apple (Mac, iPhone and iPad), Google Android, RIM Blackberry and Microsoft (Windows and Windows Phone7). If a customer buys a book from the Kindle store, it can be read on most of the major platforms for a single fee.
Amazon doesn’t break out sales data for either Kindle or eBooks, but the following extract from Amazon’s 4Q 2010 earnings release provides just an indication of progress being made.
Amazon.com is now selling more Kindle books than paperback books. Since the beginning of the year, for every 100 paperback books Amazon has sold, the Company has sold 115 Kindle books. Additionally, during this same time period the Company has sold three times as many Kindle books as hardcover books. This is across Amazon.com’s entire U.S. book business and includes sales of books where there is no Kindle edition. Free Kindle books are excluded and if included would make the numbers even higher.
The Company sold millions of third-generation Kindle devices with the new advanced paper-like Pearl e-ink display in the fourth quarter and the third-generation Kindle eclipsed ―Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows - as the best selling product in Amazon’s history.
The U.S. Kindle Store now has more than 810,000 books including New Releases and 107 of 112 New York Times Bestsellers. Over 670,000 of these books are $9.99 or less, including 74 New York Times Bestsellers. Millions of free, out-of-copyright, pre-1923 books are also available to read on Kindle.
January 2011’s sales figures from the American Association of Publishers also point to the growing success of eBooks - US$70m – a 116% increase year-on-year - despite a small, 1.8% (US$805m), fall in the overall market. eBook market share figures are hard to verify. Apple recently claimed 20% of the market, Barnes and Noble (US-only) also claimed 20% of the market and Amazon claims between 70% and 80% of the market - obviously not all can be true.
Wild market claims are to be expected in this high growth stage of the market development and there is uncertainty whether a 20% market share is by downloads or value and whether downloads include free, out of copyright eBooks which generate no revenue. All estimates that the STL team have seen indicate that Amazon is the market leader with a market share in the 50%-75% range. This CNET interview with Ian Freed, an Amazon vice president in charge of the Kindle, provides more detail on where Amazon sees itself in the market.
Although detailed data isn’t available about whether Amazon is yet making a contribution to operating profit from the Kindle and eBooks generally, all the indications are that Amazon is happy with the results and the continued investment speaks for itself.
The STL team believes Amazon’s success can be put down to five key factors:
The STL team believes that this last point is extremely important. Currently, Amazon has over two million sellers on its stores most of which are small businesses selling physical goods with the help of Amazon tools and services. This volume is far in excess of most developer schemes and almost certainly far larger than the combined total of content sellers across all developer platforms. Amazon will have little problem building and managing an even larger community as the developer community has largely adopted ‘Amazon Web Services’ as their cloud platform of choice, and sellers are already familiar and happy with Amazon tools and services.
In the UK for example, Amazon share of the overall music retail market was a healthy 13.4% in 2009. Overall, the internet players have the largest share of the music market with 39%, compared to specialist retailers, such as HMV, with 33% and Supermarkets, such as Tesco and Sainsbury’s, with 23.6%. In a decade, the internet as an e-commerce channel has overtaken all of the UK’s high street. The download only Apple iTunes service with share of 10.6% clearly dominates the online distribution market.
Figure 7: Amazon’s Music Share is Healthy but not Dominant
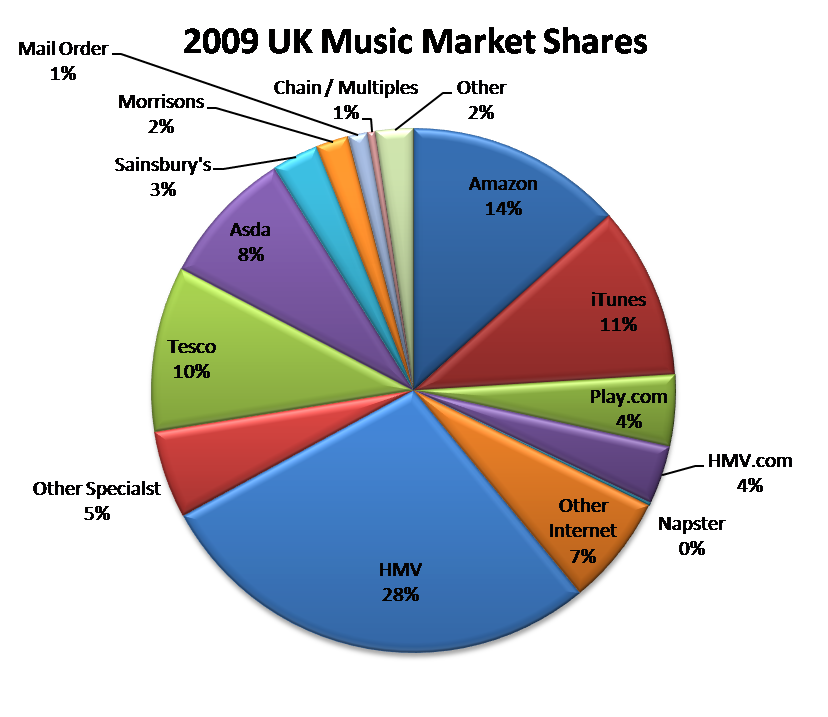
Source: BPI Yearbook 2009
In the USA, Billboard estimated that in 2009 iTunes had 26.7% retail market share, which translated into 65.5% online market share. For a la carte download sales, the iTunes U.S. presence is overwhelming, with an estimated 93% market share.
In contrast, Amazon's MP3 store had an overall 1.3% market share, which translates into about 5% share for a la carte downloads. Amazon commenced digital downloads in 2007 and has been a constant innovator.
The service launched with DRM-free tracks which were therefore portable between devices and with higher bitrate encoding, providing higher quality to the discerning ear. In the USA, the catalogue has continually grown and from an initial 2m tracks have grown to today having 1.4m albums and 15.2m tracks. But, as befits its corporate strategy of “everyday low pricing”, Amazon has put most effort into price innovation.
Figure 8: Amazon’s Smart Targeting & Competitive Pricing
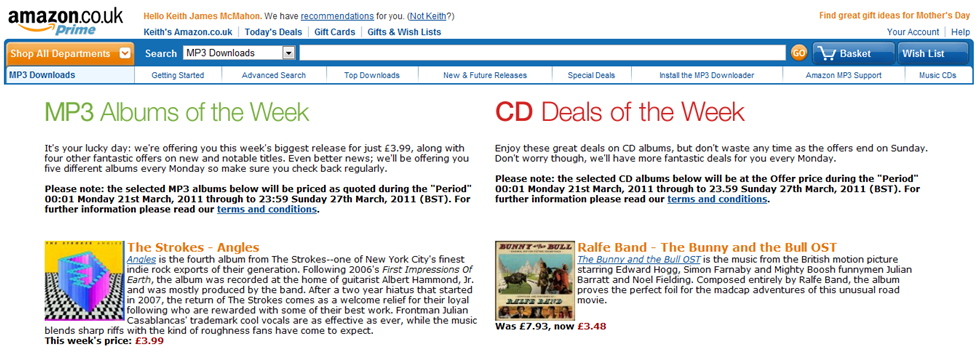
Normally, Amazon has the lowest price for its chosen Album of the week. For instance, The Strokes new album is currently available for £4 compared to iTunes pricing of £8 in the UK. This is typical behaviour of a master retailer driving customers to their stores through headline offers and promotions to their customers. Apple has a very different approach relying on an agency model where the content owner has limited choice in setting retail prices.
In the USA, Amazon's Daily Deal launched in June 2008 and it became the subject of a Department of Justice (DOJ) inquiry in May 2010 after iTunes began grumbling about Amazon promotions to the major labels. No comment has been released by the DOJ, but it seems clear that with Apple’s huge iTunes share that any attempt to discourage labels from participating in the Amazon promotions might be construed as price fixing. Amazon has continued to play its strongest card – differentiation though price competition.
Amazon has built an MP3 application for Android phones which allows the immediate purchase and playing of songs. It is noticeable that they haven’t built the same tools for Apple. In fact, the Amazon WindowShop application for the iPad actually displays download prices (and the playing of short clips), but doesn’t allow the direct purchase or download. Given, Apple’s domination of the music download market and the fact that Apple have allowed the Kindle store to operate on the iPad/iPhone, the STL team predict it will not be long before the DOJ launch another inquiry into Apple’s music practices.
In contrast to eBooks, Amazon does not seem to have built significant music share and the STL team puts this down to three main reasons:
Amazon has taken a different approach to Movies than to either Books or Music.
In the UK and Germany, Amazon has recently acquired full ownership of a DVD and streaming service, called LoveFilm. This operates primarily under a subscription model providing access to a library of films. It is the UK and German equivalent of Netflix.
A subscription business operates under a vastly model than a retailer. It requires a much larger investment in both customer acquisition and retention and in content libraries. There is also reasonable investment required in gaining access and building clients for the plethora of devices coming onto the market to connect TVs to the internet. It also starts to compete with powerful payTV companies that have very deep pockets, large customer bases and similar ambitions.
In the USA, Netflix has managed to build a strong base of customers, a large market capitalization and is currently a darling of both the press and the investor community. The STL team has written extensively in the past about Netflix, its business model and prospects (see: The Impact of Netflix: Can Telcos Help Hollywood; Entertainment 2.0: New Sources of Revenu for Telcos?)
Amazon has decided to enter the fray in the USA with its Instant Video service. This service offers a limited selection of free streaming movies to subscribers of the Amazon Prime service. The Amazon Prime service is priced at US$79/per annum, compared to the Netflix streaming cost of US$8/month ($96/annum). Although, the annual fee may put some off, Amazon seems to have solved the problem of expensive customer acquisition. However, it is questionable whether Amazon under a licensing structure can afford similar levels of investment in content as Netflix.
A key factor in deciding this will be the support of studios for its model and their willingness to provide premium content and in this Amazon is gaining traction.
Figure 9: New Releases are Going to Amazon First
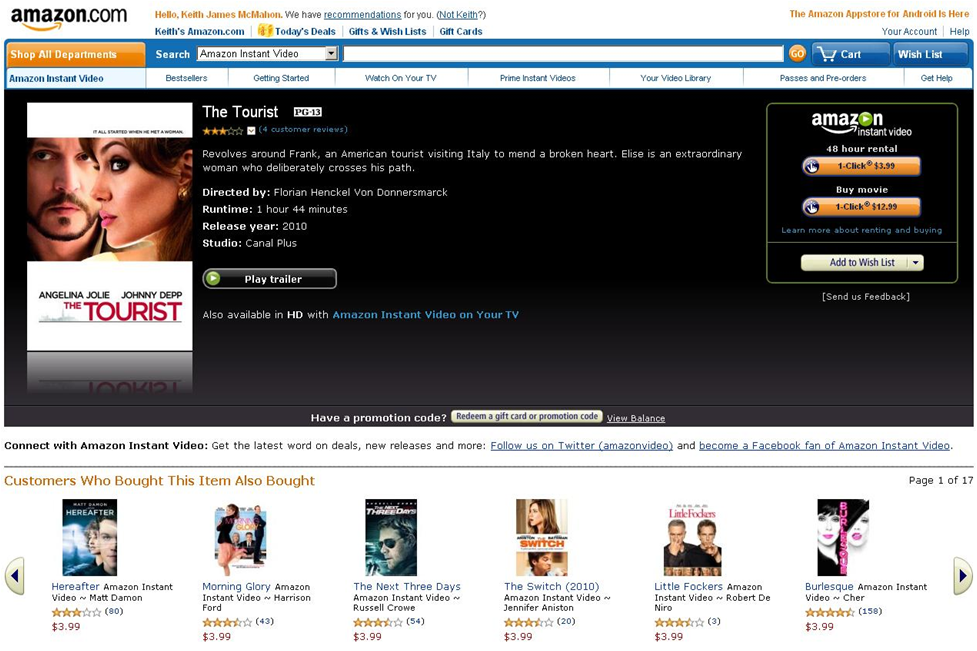
It is noticeable in the USA that Amazon are heavily promoting download-to-rent and download-to-own options which brings new releases to the library and are favoured by the Movie Industry.
Amazon is also an UltraViolet member which again we have written extensively about (see Telcos Risk Missing the UltraViolet Online Opportunity) and it is likely in the near future that Amazon will sell physical DVDs with the right to stream to multiple devices.
In Movies, STL Partners believes Amazon is uncertain which of the options will win in the future and is willing to invest in a wide range of options; effectively, it’s hedging its bets. But as in Music, Amazon has a long way to catch up with early platforms, whether that’s Apple, which leads the download-to-rent and own market, or Netflix which leads the subscription business. Again, this makes it an interesting target for partnerships, particularly for content owners looking to establish models that work better for them than Apple or Netflix.
Amazon also has a significant business selling both physical electronic games and consoles. It was therefore hardly surprising that it launched Android AppStore heavily populated with games and featuring Angry Birds Rio as its launch game.
Figure 10: Amazon’s Appstore
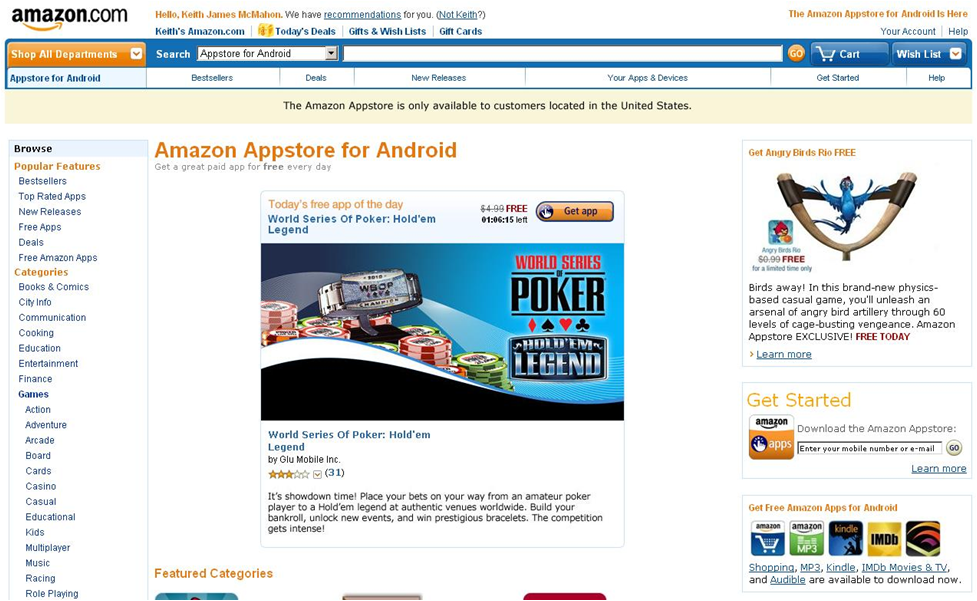
The Amazon AppStore offers some very interesting features, including:
There are also teething problems with the service. For example, the Amazon AppStore is impossible to install on some “locked-down” Android handsets.
But Amazon has entered the market and the STL team believes it will be a serious player for years to come. It is also our belief that Amazon will want to develop AppStores for all major platforms, which will bring them into considerable conflict with certain platform owners, not just Apple.
To read the report in full, including the conclusions and recommendations...
...Members of the Telco 2.0TM Executive Briefing Subscription Service and the Dealing with Disruption Stream can access and download a PDF of the full report here. Non-Members, please see here for how to subscribe. Alternatively, please email contact@telco2.net or call +44 (0) 207 247 5003 for further details. 'Growing the Mobile Internet' and 'Lessons from Apple: Fostering vibrant content ecosystems' are also featured at our AMERICAS and EMEA Executive Brainstorms and Best Practice Live! virtual events.