|
| Summary: Telefonica and Vodafone are both European-based tier 1 CSPs with substantial revenues, cash flows and subscribers. They have both expanded beyond Europe – Vodafone into Africa and Asia and Telefonica into Latin America. However, their Telco 2.0 strategies are rather different. In this extract from our forthcoming report, A Practical Guide to Implementing Telco 2.0, we outline their Telco 2.0 strategies and their benefits and risks. (September 2012, Executive Briefing Service, Transformation Stream.) |
|
Below is an extract from this 14 page Telco 2.0 report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing service and the Telco 2.0 Transformation Stream here. Non-members can subscribe here.
This report is itself an edited section taken from our forthcoming strategy report, A Practical Guide to Implementing Telco 2.0. We will be sharing some of the findings, and exploring them in the market context at Digital Arabia, the Telco 2.0 invitation only Executive Brainstorm taking place in Dubai, 6-7 November, in and Digital Asia in Singapore, 3-5 December, 2012.
To find out more about any of these services, apply for an invitation to the Brainstorms, and for any other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
To share this article easily, please click:
Two Different Telco 2.0 Strategies
‘Full Service Telco 2.0’ Vs. Telco 2.0 ‘Happy Piper’
In our reports the ‘Roadmap to New Telco 2.0 Business Models’ and ‘A Practical Guide to Implementing Telco 2.0’, we identify two archetypal Telco 2.0 strategies: ‘Full Service Telco 2.0’; and ‘Telco 2.0 Happy Piper’.
Figure 1 - Porter and Telco 2.0 competitive strategies
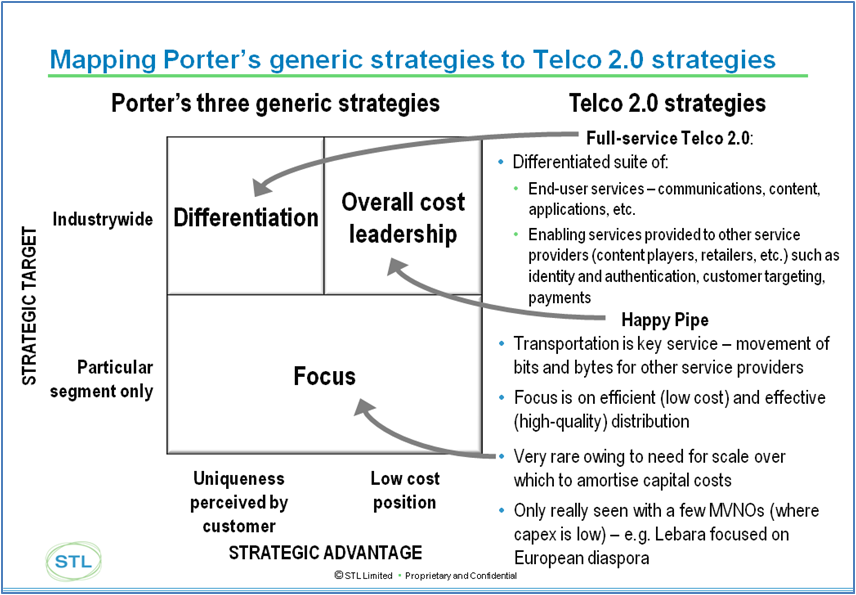
Source: Michael Porter / STL Partners / Telco 2.0
- ‘Full-Service Telco 2.0’. In this ‘two-sided’ business model, CSPs have two clear customer groups: end-users and other 3rd Party Organisations who interact with end-users (what we call ‘Upstream’ companies – banks, retailers, advertisers, government, utilities, software developers other telcos). CSPs seek to compete with each other and with others, such as the ‘internet players’, by differentiating both in the end-user services (communications, content, etc.) and with the enabling services they provide to other service providers (identity and authentication, customer targeting/marketing services, payments, customer care, and so forth).
- The ‘Telco 2.0 Happy Piper’. CSPs that pursue this strategy will focus on retail or wholesale connectivity to upstream and/or downstream customers rather than on higher-level (value-added) services. It is worth noting that although simplicity and cost control are key themes of the ‘Telco 2.0 Happy Piper’, there remains scope for revenue growth through providing ‘enhanced connectivity’ options.
Overview: Telefonica 2.0 and Vodafone 2.0
At a top-level, Telefonica is pursuing a ‘Telco 2.0 Service Provider’ strategy whereas Vodafone, although dabbling in Telco 2.0 services, is largely committed to a defensive approach to digital services (protecting voice and messaging) and is aggressively pursuing a ‘Happy Piper’ strategy. We illustrate a qualitative assessment of where the two CSPs sit on the Happy Piper-Service Provider continuum, together with a selection of other CSPs in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Positioning CSPs on the Happy Piper - Service Provider continuum

Source: STL Partners / Telco 2.0
Telefonica: Telco 2.0 Service Provider
Background: Digital Innovator
STL Partners believes that Telefonica is arguably the most advanced operator globally in moving from traditional telecoms (Telco 1.0) to a Telco 2.0 Service Provider strategy. This belief was reinforced by the reorganisation in Autumn 2011 in which Matthew Key, the European CEO, was appointed head of a new unit, Telefonica Digital, which has the objective to build the company’s presence and value in the digital world. A press release in September 2011 summarised the objectives of the division as being:
- To take full advantage of the opportunities afforded by the digital world with respect to new products, services and value chains, both in markets where the company operates directly and those in which it has industrial alliances or the potential to operate directly in OTT (over the top) businesses.
- This unit will be responsible for developing and globally exploiting businesses like, among others, video and entertainment, e-advertising, e-health, financial services, cloud and M2M. It will aim its activity both at the corporate and residential segments.
- To actively help the two major geographic regions, Europe and Latin America, take advantage of their distinguishing traits (relationship with and proximity to more than 300 million customers, capillarity, invoicing and distribution capabilities).
- To attain this goal, the unit will develop top-flight global competencies in the areas of business intelligence, pricing strategies and management of alliances in the digital environment with respect to both hardware (i.e. devices) and software.
- Generate new growth opportunities by investing in new digital businesses, while grouping together or reinforcing initiatives such as Amerigo, Wayra and Vc's.
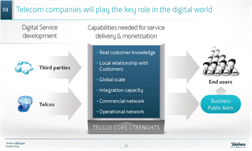
Figure 3: Telefonica’s Telco 2.0 Service Provider strategy
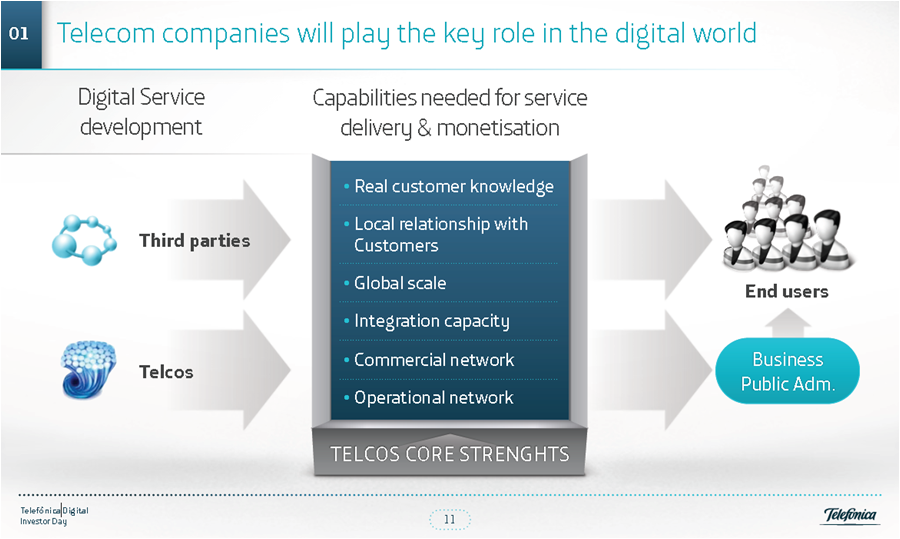
Source: Telefonica
Telefonica Digital is a significant development in the company’s commitment to Telco 2.0 services for three reasons:
- For the first time a CSP has been transparent about how much revenue it is generating from non-traditional ‘digital’ services. In 2011, Telefonica Digital generated revenue of €2.4 billion and intends to grow this by around 20% a year to reach around €5 billion in 2015.
- Telefonica Digital is a relatively autonomous entity with separate headquarters (in London rather than Slough) and separate product and service development capabilities. It can both leverage Telefonica’s commercial distribution capabilities (via the operating companies) and, crucially, distribute services over-the-top via app stores and the internet. Essentially, it has been given the authority to compete with the core business as an in-house ‘OTT player’.
- It is specifically focused on the services layer – both end-user services and enabling services for third-party service providers (including advertising and security). It will leverage Telefonica’s network where it makes sense to do so (e.g. for M2M) but will not be tied to the network if it makes sense to build OTT services (e.g. Tu Me, one of its OTT voice services, is available for non-Telefonica customers). It also seeks to buy (e.g. Terra, Tuenti), build (e.g. Priority Moments) and partner (via various models including Wayra, in which Telefonica makes seed capital available to early stage businesses).
Figure 4: Telefonica’s Telco 2.0 service portfolio

Source: Telefonica
To read the note in full, including the following additional sections detailing support for the analysis...
- Telefonica's Telco 2.0 products and services
- Vodafone's approach
- Background: safety first
- Vodafone's Telco 2.0 services
- Vodafone One Net: Unified Communications in the Cloud for SMBs
- Vodafone Freebees: Retaining the Pre-pay base
- Summary: Strategic Evaluation
...and the following figures...
- Figure 1 - Porter and Telco 2.0 competitive strategies
- Figure 2: Positioning CSPs on the Happy Piper - Service Provider continuum
- Figure 3: Telefonica’s Telco 2.0 Service Provider strategy
- Figure 4: Telefonica’s Telco 2.0 service portfolio
- Figure 5: Vodafone – main messages are about being an efficient data pipe
- Figure 6: Vodafone One Net – a defensive play in the SMB market
- Figure 7: Telefonica and Vodafone Telco 2.0 strategies – evaluation
...Members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing Subscription Service and the Telco 2.0 Transformation Stream can download the full 14 page report in PDF format here. Non-Members, please subscribe here. For this or other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
Companies and Technologies Featured: Vodafone, Telefonica, O2, Priority Moments, Top-Up Surprises, Freebees, Tu Me, Tuenti, Terra, OneNet, Wayra, M2M, OTT, Jajah, Happy Piper, Full Service, Telco 2.0.



