| Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) such as Akamai’s are used to improve the quality and reduce costs of delivering digital content at volume. What role should telcos now play in CDNs? (September 2011, Executive Briefing Service, Future of the Networks Stream). |
|
Below is an extract from this 19 page Telco 2.0 Report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing service and Future Networks Stream here. Non-members can subscribe here, buy a Single User license for this report online here for £795 (+VAT), or for multi-user licenses or other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
To share this article easily, please click:We've written about Akamai’s technology strategy for global CDN before as a fine example of the best practice in online video distribution and a case study in two-sided business models, to say nothing of being a company that knows how to work with the grain of the Internet. Recently, Akamai published a paper which gives an overview of its network and how it works. It’s a great paper, if something of a serious read. Having ourselves read, enjoyed and digested it, we’ve distilled the main elements in the following analysis, and used that as a basis to look at telcos' opportunities in the CDN market.
In the strategy report Mobile, Fixed and Wholesale Broadband Business Models - Best Practice Innovation, ‘Telco 2.0' Opportunities, Forecasts and Future Scenarios we examined a number of different options for telcos to reduce costs and improve the quality of content delivery, including Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
This followed on from Future Broadband Business Models - Beyond Bundling: winning the new $250Bn delivery game in which we looked at long term trends in network architectures, including the continuing move of intelligence and storage towards the edge of the network. Most recently, in Broadband 2.0: Delivering Video and Mobile CDNs we looked at whether there is now a compelling need for Mobile CDNs, and if so, should operators partner with existing players or build / buy their own?
We’ll also be looking in depth at the opportunities in mobile CDNs at the EMEA Executive Brainstorm in London on 9-10th November 2011.
The basic CDN concept is simple. Rather than sending one copy of a video stream, software update or JavaScript library over the Internet to each user who wants it, the content is stored inside their service provider's network, typically at the POP level in a fixed ISP.
That way, there are savings on interconnect traffic (whether in terms of paid-for transit, capex, or stress on peering relationships), and by locating the servers strategically, savings are also possible on internal backhaul traffic. Users and content providers benefit from lower latency, and therefore faster download times, snappier user interface response, and also from higher reliability because the content servers are no longer a single point of failure.
What can be done with content can also be done with code. As well as simple file servers and media streaming servers, applications servers can be deployed in a CDN in order to bring the same benefits to Web applications. Because the content providers are customers of the CDN, it is possible to also apply content optimisation with their agreement at the time it is uploaded to the CDN. This makes it possible to save further traffic, and to avoid nasty accidents like this one.
Once the CDN servers are deployed, to make the network efficient, they need to be filled up with content and located so they are used effectively – so they need to be located in the right places. An important point of a CDN, and one that may play to telcos’ strengths, is that location is important.
Figure 1: With higher speeds, geography starts to dominate download times
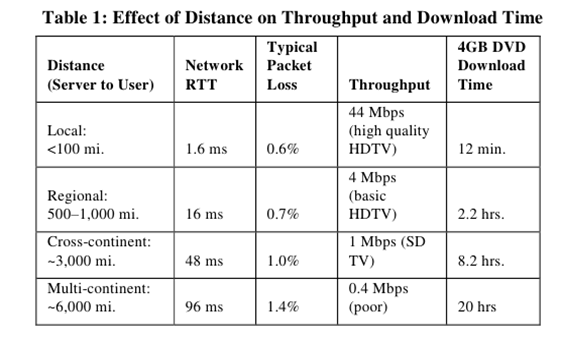
Source: Akamai
CDNs are a diverse group of businesses, with several major players, notably Akamai, the market leader, EdgeCast, and Limelight Networks, all of which are pure-play CDNs, and also a number of players that are part of either carriers or Web 2.0 majors. Level(3), which is widely expected to acquire the LimeLight CDN, is better known as a massive Internet backbone operator. BT Group and Telefonica both have CDN products. On the other hand, Google, Amazon, and Microsoft operate their own, very substantial CDNs in support of their own businesses. Amazon also provides a basic CDN service to third parties. Beyond these, there are a substantial number of small players.
Akamai is by far the biggest; Arbor Networks estimated that it might account for as much as 15% of Internet traffic once the actual CDN traffic was counted in, while the top five CDNs accounted for 10% of inter-domain traffic. The distinction is itself a testament to the effectiveness of CDN as a methodology.
As an example of the benefits of their CDN, above and beyond ‘a better viewing experience’, Akamai claim that they can demonstrate a 15% increase in completed transactions on an e-commerce site by using their application acceleration product. This doesn’t seem out of court, as Amazon.com has cited similar numbers in the past, in their case by reducing the volume of data needed to deliver a given web page rather than by accelerating its delivery.
As a consequence of these benefits, and the predicted growth in internet traffic, Akamai expect traffic on their platform to reach levels equivalent to the throughput of a US national broadcast TV station within 2-5 years. In the fixed world, Akamai claims offload rates of as much as 90%. The Jetstream CDN blog points out that mobile operators might be able to offload as much as 65% of their traffic into the CDN. These numbers refer only to traffic sources that are customers of the CDN, but it ought to be obvious that offloading 90% of the YouTube or BBC iPlayer traffic is worth having.
In Broadband 2.0: Mobile CDNs and video distribution we looked at the early prospects for Mobile CDN, and indeed, Akamai's own move into the mobile industry is only beginning. However, Telefonica recently announced that its internal, group-wide CDN has reached an initial capability, with service available in Europe and in Argentina. They intend to expand across their entire footprint. We are aware of at least one other mobile operator which is actively investing in CDN capabilities. The degree to which CDN capabilities can be integrated into mobile networks is dependent on the operator’s choice of network architecture, which we discuss later in this note.
It's also worth noting that one of Akamai's unique selling points is that it is very much a global operator. As usual, there's a problem for operators, especially mobile operators, in that the big Internet platforms are global and operators are regional. Content owners can deal with one CDN for their services all around the world – they can’t deal with one telco. Also, big video sources like national TV broadcasters can usually deal with one ex-incumbent fixed operator and cover much of the market, but must deal with several mobile operators.
Akamai is already doing a lot of what we call "ADN" (Application-Delivery Networking) by analogy to CDN. In a CDN, content is served up near the network edge. In an ADN, applications are hosted in the same way in order to deliver them faster and more reliably. (Of course, the media server in a CDN node is itself a software application.) And the numbers we cited above regarding improved transaction completion rates are compelling.
However, we were a little under-whelmed by the details given of their Edge Computing product. It is restricted to J2EE and XSLT applications, and it seems quite limited in the power and flexibility it offers compared to the state of the art in cloud computing. Google App Engine and Amazon EC2 look far more interesting from a developer point of view. Obviously, they're going for a different market. But we heartily agree with Dan Rayburn that the future of CDN is applications acceleration, and that this goes double for mobile with its relatively higher background levels of latency.
Interestingly, some of Akamai's ADN customers aren't actually distributing their code out to the ADN servers, but only making use of Akamai’s overlay network to route their traffic. Relatively small optimisations to the transport network can have significant benefits in business terms even before app servers are physically forward-deployed.
There are some shifts underway in the CDN landscape. Notably, as we mentioned earlier, there are rumours that Limelight Networks wants to exit the packet-pushing element of it in favour of the media services side - ingestion, transcoding, reporting and analytics. The most likely route is probably a sale or joint venture with Level(3). Their massive network footprint gives them both the opportunity to do global CDNing, and also very good reasons to do so internally. Being a late entrant, they have been very aggressive on price in building up a customer base (you may remember their role in the great Comcast peering war). They will be a formidable competitor and will probably want to move from macro-CDN to a more Akamai-like forward deployed model.
To read the note in full, including the following additional analysis......and the following charts...
...Members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing Subscription Service and Future Networks Stream can download the full 19 page report in PDF format here. Non-Members, please subscribe here, buy a Single User license for this report online here for £795 (+VAT), or for multi-user licenses or other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
Organisations, people and products referenced: 3UK, Akamai, Alcatel-Lucent, Amazon, Arbor Networks, BBC, BBC iPlayer, BitTorrent, BT, Cisco, Dan Rayburn, EC2, EdgeCast, Ericsson, Google, GSM, Internet HSPA, Jetstream, Level(3), Limelight Networks, MBNL, Microsoft, Motorola, MOVE, Nokia Siemens Networks, Orange, TalkTalk, Telefonica, T-Mobile, Velocix, YouTube.
Technologies and industry terms referenced: 3GPP, ADSL, App Engine, backhaul, Carrier-Ethernet, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), DNS, DOCSIS 3, edge computing, FTTx, GGSN, Gi interface, HFC, HSPA+, interconnect, IT, JavaScript, latency, LTE, Mobile CDNs, online, peering, POPs (Points of Presence), RNC, SQL, UMTS, VPN, WLAN.