| Summary: The telecoms industry often puts so-called OTT (over-the-top) players like Google and Facebook at the forefront of its concerns, as they pose new competition for services and applications. But what about encroachment of companies “underneath” the telcos, displacing them from their core asset, the network? Telco 2.0 examines the strategic threats and opportunities from wholesale providers, outsourcers and government-run broadband networks. (January 2012, Executive Briefing Service, Future of the Networks Stream). |
|
Below is an extract from this 32 page Telco 2.0 Report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing service and Future Networks Stream here. Non-members can subscribe here, buy a Single User license for this report online here for £795 (+VAT for UK buyers), or for multi-user licenses or other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
To share this article easily, please click:In some quarters of the telecoms industry, the received wisdom is that the network itself is merely an undifferentiated “pipe”, providing commodity connectivity, especially for data services. The value, many assert, is in providing higher-tier services, content and applications, either to end-users, or as value-added B2B services to other parties. The Telco 2.0 view is subtly different. We maintain that:
Either through deliberate actions such as outsourcing, or through external agency (Government, greenfield competition etc), we see the network-part of the telco universe suffering from a creeping loss of control and ownership. There is a steady move towards outsourced networks, as they are shared, or built around the concept of open-access and wholesale. While this would be fine if the telcos themselves remained in control of this trend (we see significant opportunities in wholesale and infrastructure services), in many cases the opposite is occurring. Telcos are losing control, and in our view losing influence over their core asset – the network. They are worrying so much about competing with so-called OTT providers that they are missing the threat from below.
At the point at which many operators, at least in Europe and North America, are seeing the services opportunity ebb away, and ever-greater dependency on new models of data connectivity provision, they are potentially cutting off (or being cut off from) one of their real differentiators.
Given the uncertainties around both fixed and mobile broadband business models, it is sensible for operators to retain as many business model options as possible. Operators are battling with significant commercial and technical questions such as:
Answers to these and other questions remain opaque. However, it is clear that many of the potential future business models will require networks to be physically or logically re-engineered, as well as flexible back-office functions, like billing and OSS, to be closely integrated with the network.
Outsourcing networks to third-party vendors, particularly when such a network is shared with other operators is dangerous in these circumstances. Partners that today agree on the principles for network-sharing may have very different strategic views and goals in two years’ time, especially given the unknown use-cases for new technologies like LTE.
This report considers all these issues and gives guidance to operators who may not have considered all the various ways in which network control is being eroded, from Government-run networks through to outsourcing services from the larger equipment providers.
Figure 1 - Competition in the services layer means defending network capabilities is increasingly important for operators 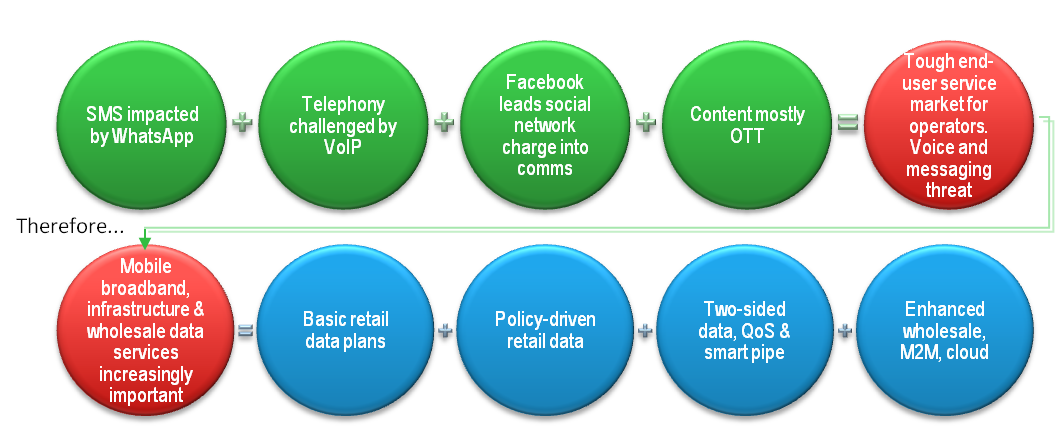
Source: STL Partners
Over the last year, Telco 2.0 has updated its overall map of the telecom industry, to reflect ongoing dynamics seen in both fixed and mobile arenas. In our strategic research reports on Broadband Business Models, and the Roadmap for Telco 2.0 Operators, we have explored the emergence of various new “buckets” of opportunity, such as verticalised service offerings, two-sided opportunities and enhanced variants of traditional retail propositions.
In parallel to this, we’ve also looked again at some changes in the traditional wholesale and infrastructure layers of the telecoms industry. Historically, this has largely comprised basic capacity resale and some “behind the scenes” use of carriers-carrier services (roaming hubs, satellite / sub-oceanic transit etc).
Figure 2 - Telco 1.0 Wholesale & Infrastructure structure
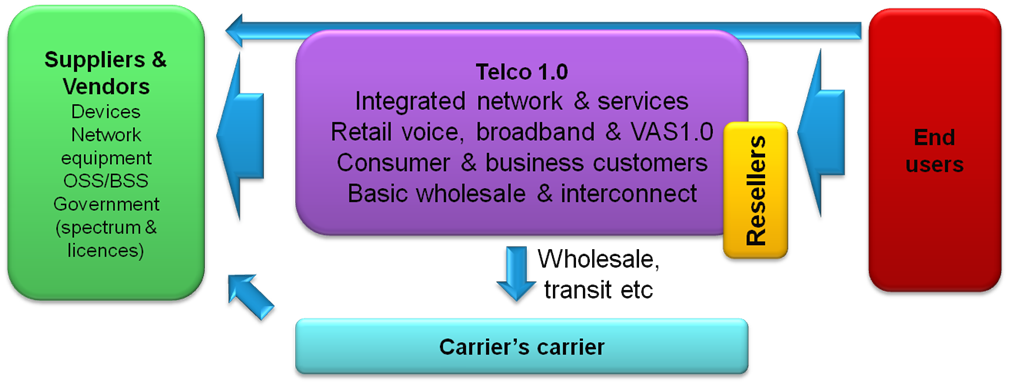
Source: STL Partners
To read the note in full, including the following additional analysis...
...Members of the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing Subscription Service and Future Networks Stream can download the full 32 page report in PDF format here. Non-Members, please subscribe here, buy a Single User license for this report online here for £795 (+VAT for UK buyers), or for multi-user licenses or other enquiries, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
Organisations, geographies, people and products referenced: 3UK, Aero2, Alcatel-Lucent, Apple, Arbinet, Australia, Belgacom ICS (International Carrier Services), Bell, Bharti Airtel, BT, BT Retail, Canada, Citynet, Clearwire, Crown Castle, Deutsche Telekom, Eircom, Ericsson, Europe, EverythingEverywhere, Facebook, FLAG, France Telecom, Global Crossing, Google, Government, Green Packet, Huawei, Hutchison 3 Australia, iBasis, identity and authentication, identity services, India, Inmarsat, Intel, Intelsat, Interoute, IPX (Internet Payment Exchange), Ireland, Kenya, KPN, Level 3, LightSquared, Malaysia, Mexico, Microsoft, MVS Comunicaciones, Netherlands, Nortel, North America, OpenReach, Optism, Optus, Orange, Orange Switzerland, Poland, ProgrammableWeb, Qualcomm, Reggefiber, Russia, Sferia, SFR, Singapore, Skype, Spain, Sprint, Sunrise, Sweden, Switzerland, Tele2, Telenor, Tellabs, Telstra, Telus, T-Mobile, T-Mobile USA, UK, UQ/KDDI, Velocix, Verizon, Vodafone, WhatsApp, Wireless@SG, Yota, ZTE. .
Technologies and industry terms referenced: 4G, advertisers, APIs, applications, B2B services, backhaul, bandwidth, billing, broadband, Carrier ethernet, CDNs, cloud, content delivery, customer care, customer data, dark fibre, dumb pipes, email, EPC (Evolved Packet Core), femtocells, fibre deployment, FTTH, greenfield, healthcare, IMS, infrastructure, Internet peering exchanges, IP cellular networks, local loop unbundling (LLU), LTE, M2M, mobile, MOCN (Multi Operator Core Network), MORAN (Multi Operator Radio Access Network), MVNO, NEPs, Net Neutrality, network, network congestion, network policy, offload/onload models, OSS, OTT, outsourcing, payments, personalisation, probes, Quality of Experience (QoE), Quality of Service (QoS), real-time gaming, regulation, roaming, roaming hubs, satellite / sub-oceanic transit, site-sharing, smart grids, smart network, social networks, spectrum, streamed movie, structural separation, targeting, Telco 1.0 business model, text, Tower-sharing, traffic management, TV/cable, two-sided business models, Under-the-Floor players (UTF),vertical services, video call, voice telephony, web hosting, wholesale, wholesale ADSL, WiFi, WiMAX.