Report Summary: This 120 page Strategy Report focuses on the ‘Digital Generation’ - the cohort which has grown up with new applications and technologies - whose behaviour will ultimately drive the future shape of the Telco business.
This report is now availalable to members of our Telco 2.0 Research Executive Briefing Service. Below is an introductory extract and list of contents from this strategy Report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the executive Briefing Service here.
For more on any of these services, please email / call +44 (0) 207 247 5003
The Digital Generation wants:
Telcos want:
The Digital Generation has integrated some technologies and applications with their lives and discarded the rest - those that don't fit - rapidly. Many other applications and services familiar to our readers (Facebook, QQ, Apple, Google, etc) now serve some of the needs that Telcos alone used to serve.
Telcos have generally been slow to produce services that meet the needs and expectations of these customers. Unchecked, this will ultimately lead to the disintermediation of the telcos from their ultimate source of value - their customers. This is a strategic threat not just for the youth segment but ultimately across all generations. This report outlines the threat, the urgent need for change, and a framework to support that change.
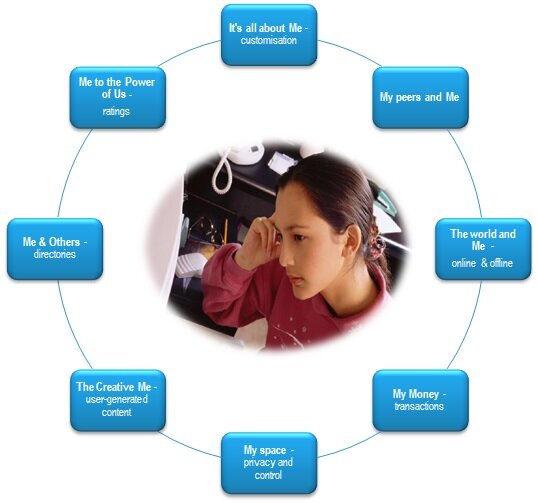
In previous STL Part.ners' reports the focus has been on how Telco assets could be used to open new revenue streams from upstream service providers wanting to interact with end-users. Reports such as the 2-Sided Telecoms Market Opportunity have focused upon the business opportunity of how operators could reduce digital friction and protect themselves from over the top providers eager to circumvent the operator and gain access to the end-user directly.
In this report we shift the focus to examine end-users and their behaviours, explaining how:
Serving the Digital Generation focuses on why and how young people are adopting digital and communication technologies into their lives. By doing this, STL Partners can help Telco industry management better anticipate, and respond to, the main drivers and unmet needs of tomorrow's Telco 2.0 customer. What we may regard as quirky segmented behaviour today (blogging, twittering, social networking, for example) is, in fact, mass consumer behaviour tomorrow. Here STL Partners gives an insight into mass-market behaviours for a new breed of customer, which will shape the future of the communications and media sectors.
This report explains this behaviour and explores how the desire to participate represents a new opportunity for Telco value creation. To realise this opportunity, we have developed a new framework for future product development and services, The Customer Participation Framework (CPF). Developed initially as a template for validating new service or application ideas, the CPF is a tool that can be used to support different phases of the product or service innovation process:
At concept initiation, to validate ideas against customer needs;
During the development and trial phase, to ensure usability issues are properly addressed;
In the execution phase, as a means of feedback iteration and a measurement of success.
The CPF framework can help operators increase the value of the Telco Value-Added Services platform and lead to entirely new ways of defining, evaluation, developing and marketing Telco services (retail) to both upstream service providers/partners and end users.We believe that The Customer Participation Framework represents an opportunity for operators to increase the value of their platforms and retail strategies and thus help to realise the $375billion two-sided business opportunity outlined in the 2-Sided Telecoms Market Opportunity and the Future Broadband Business Model reports.
The report is for senior (CxO) decision-makers and business strategists, product managers, strategic sales, business development and marketing professionals acting in the following types of organisations:
Strategists and CxOs in IT and Investment Companies may also find this report useful to understand the future landscape of the Telecoms and related industries, and to help to spot likely winning and losing investment and operational strategies in the market.
During the period of rapid growth when markets were emerging, the process of product or service development for Telcos was driven by a focus on network roll out, capacity issues, spectrum licences, supply chains, vendors, traffic forming, the regulatory environment and so on.
This was understandable. Uptake of Telco services was rapid and the challenges of meeting demand immense. Innovation was predominantly in hardware, which required long development cycles, massive investments and a stable regulatory environment. Everything was tested to destruction to ensure robustness and the ability to scale. The industry thrived, driven by some outstanding innovations in core networks, capacity handling etc.
Today, however, as markets mature and become saturated, this approach to innovation has run its course.
Increasingly, core propositions and networks are being commoditised and new services are being developed and delivered by others over the Telco infrastructure. Operators are under increased pressure to:
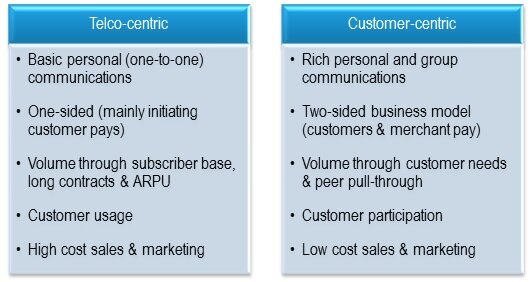
But to build stronger customer experience and innovate in new spheres, requires a shift in focus from being Telco-centric to customer-centric. Placing end-user engagement and participation at the forefront of what Telcos do requires a cultural revolution.
It means a change in processes and the revaluation of core assets.This report focuses on what areas of innovation operators should seek to focus on in their existing retail operations, as well as the core enabling services that form a cornerstone of the future business models.
We interviewed senior marketing and product development executives in a dozen operators to fully understand the how the current innovation process is managed and what evaluation criteria are adopted when developing potential new propositions, products and services. This helped us to identify the shortcomings of current innovation approaches, rooted in a tradition of network deployment and subscriber acquisition.
For our other stream of research, we drew on the extensive body of existing industry and academic research into young people's use of digital communications technology and their adoption of social software. We looked at what they are doing with technology and how adoption has occurred (including exploring nine case study examples).
This report is now available to members of our Telco 2.0 Research Executive Briefing Service. Below is an introductory extract and list of contents from this strategy Report that can be downloaded in full in PDF format by members of the executive Briefing Service here. To order or find out more please email , call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.