How telcos, banks, Internet players and media companies can make money from SoLoMo services
| This report will show telcos, banks, Internet players and media companies how to best harness the potential of mobile to take the friction out of local commerce, earn a share of the hundreds of billions of dollars merchants spend on marketing, and gain a strong strategic position in the broader digital commerce value chain. It contains unique insights building on our seven year progamme of research into digital business model innovation and cross-sector activities, including the Telco 2.0 Initiative, the New Digital Economics Brainstorm series, the WEF's 'Rethinking Personal Data' project, and global industry digital commerce projects. (September 2013). |
 |
To share this article easily, please click:
Contains:
|
Pricing and Features
|
- What are the roles and strategies for success in mobile commerce?
- Revenue and value streams, competitive landscape and key players
- Role of regulation and the value of local propositions
- Key success factors for merchant and consumer propositions
- What technologies and internal value networks are needed to deliver value?
- External ecosystem and how to partner
- Cutting-edge best practice examples
|
- PDF Format
- 100+ Pages, 50+ Charts and Tables
- For pricing, please email or call +44 (0) 207 247 5003
- NB This report is not included with the Telco 2.0 Executive Briefing Service.
|
How is this report unique?
- The report articulates comprehensive approaches to strategy in mobile commerce for telcos, banks, internet players and technology companies, identifying market positioning, propositions, finance, technology, and organisations for success.
- It is based on our digital business model analysis framework, and builds on theory and real-world experience developed through seven years of cross-industry research and activies including the Telco 2.0 Initiative, the New Digital Economics Brainstorm series, our involvement in the World Economic Forum's 'Rethinking Personal Data' project, and private industry engagements.
Who is it for?
- CEO, CMO, CSO, CIO, CTO (the board) of telcos and vendor partners.
- Digital and mobile commerce leaders and teams. strategy, marketing, product development, innovation, commercial and technical functions.
- Vendor strategy, business development and sales and marketing functions seeking to understand their clients’ changing strategic needs.
To register interest please email or call +44 (0) 207 247 5003.
Background
STL defines digital commerce as the use of new digital and mobile technologies to bring buyers and sellers together more efficiently and effectively. Fast growing adoption of mobile, social and local services is opening up opportunities to provide consumers with highly-relevant advertising and marketing services, underpinned by secure and easy-to-use payment services. By giving people easy access to information, vouchers, loyalty points and electronic payment services, smartphones can be used to make shopping in bricks and mortar stores as interactive as shopping through web sites and mobile apps.
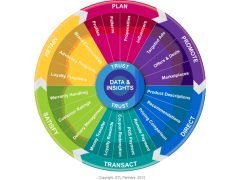
Figure 1 below summarises the 'cycle' of digital commerce, from planning, through promotion, direct marketing, transactions, customer satisfaction and retention.
Figure 1 - The Cycle and Functions of Digital Commerce

Telcos and their partners could play a major role in enabling digital commerce as intermediaries that create platforms that help to bring together buyers and sellers. But Internet companies, banks, payment networks and others are also seeking to act as digital intermediaries between merchants and consumers.
This report analyses the complex dynamics of the market and how to apply key strategies for success accounting for both global trends and local differences.
Report Contents and Structure
- Executive Summary – a five page overview of the most important takeaways.
- Chapter 1: Strategy – why it is important to secure a pivotal role in digital commerce.
- Chapter 2: Upstream value proposition– the combination of authenticated personal data (the magic ingredient) and an ubiquitous marketing platform (the smartphone).
- Chapter 3: Downstream value proposition - Putting the individual in control of the offers they receive to create a compelling customer digital commerce experience.
- Chapter 4: Internal value network – the organisational structure and expertise needed to broker digital commerce services.
- Chapter 5: External value network – who telcos need to partner with to get the flywheel started.
- Chapter 6: Technology – the authentication options (the SIM card, embedded secure domains etc.), the wallet options (apps, cloud etc. & the connectivity options (Wi-Fi, cellular, NFC, Bluetooth).
- Chapter 7: Finance – the potential revenue streams from brokering digital commerce.
- Chapter 8: Marketplace – the role of regulation and the importance of local propositions.
- Chapter 9: Cutting edge – examples of best practice in digital commerce.

